Microplastics contamination in green mussels Perna viridis in Pangkajene Kepulauan Waters, South Sulawesi, Indonesia
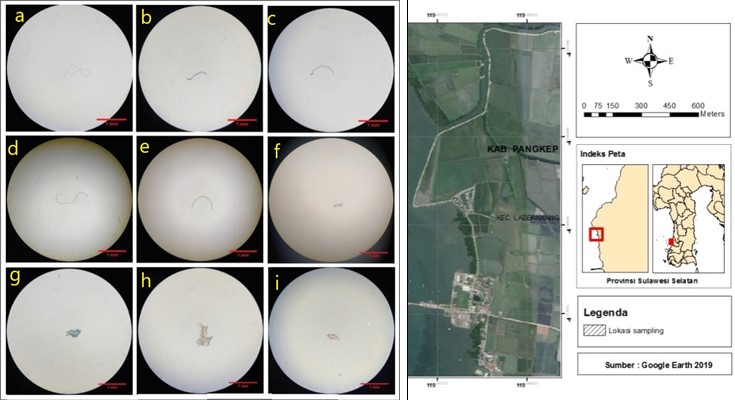
Microplastics is a problem that has been concerning, especially in marine habitat. The presence of microplastics in large quantities will have an impact on the environment and marine organisms. Marine organisms that are vulnerable to contamination by microplastics pollutants namely green mussels (Perna viridis). This study aims to determine the microplastics forms and concentration found in green mussels (Perna viridis) in Maccini Baji Waters, Labakkang District, Pangkejene Kepulauan Regency, South Sulawesi. The sampling of the mussels was carried out by the method of purposive random sampling with the sample was grouped into 3 groups of shells lengths, namely 2-3.9 cm, 4-5.9 cm and 6-7.9 cm with 33 individuals for each group. Microplastics observations were carried out using a stereo microscope. In addition to analyze microplastics concentrations, an analysis of the frequency of microplastics presence in shells was also carried out. The results showed that the microplastics was found in the form of fiber and fragments with several colors namely clear white, blue, black, red, and purple. The frequency of microplastics presence in green mussels was above 50% with an average of 71.7% exposure to microplastics. The highest frequency of microplastics presence and concentration in the range of shell lengths accounting for 2-3.9 cm.
- Ramli RamliRamli
- Khusnul YaqinKhusnulYaqin
- Nita RukminasariNitaRukminasari