Akuatikisle: Jurnal Akuakultur, Pesisir dan Pulau-Pulau Kecil
Full Length Article
Nutrient distribution models and flow patterns in Coastal Waters and Small Islands, Tanjungpinang City, Indonesia
Highlights
Generate NLP AI by Wizdam ID.
Abstract
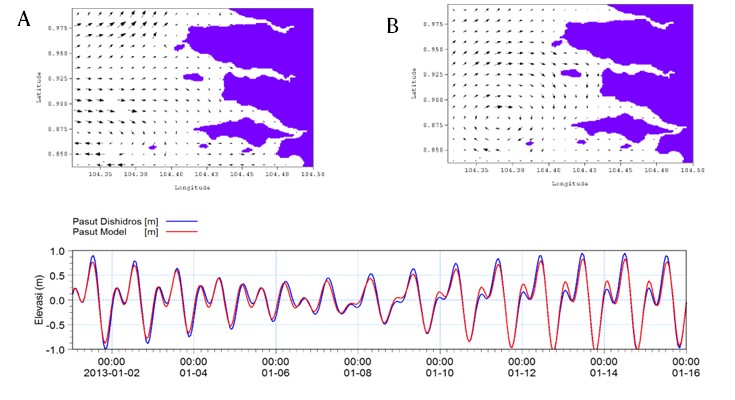
Research has been done on the model of nutrient distribution and current pattern in coastal water of Tanjungpinang City. The research objective was to develop a model of nutrient distribution and current patterns in coastal waters and small islands as an effort to manage the eutofication of coastal waters and small islands in the archipelago. Determining the location of the observations was done by purposive sampling at high tide and low tide at several predetermined research stations. The results showed the nutrient distribution model in the waters of Tanjungpinang Bay, a different distribution pattern compared to the waters of the Dompak Strait, with the distribution of nutrients from the yield model at low tide and at high tide shows the same pattern, which tends to decrease offshore and high in some coastal locations. around the waters of the Sei. Carang estuary which is connected to the waters of Tanjungpinang Bay. The pattern of currents during the highest tide is bandage and full moon in coastal waters and small islands in the area of Tanjungpinang City, which shows that the inlet flows from the west of the waters, then exits towards the north into open water. However, part of the water mass in the presence of small islands around it becomes fragmented causing a turn to the south of the coastal waters of the city of Tanjungpinang, with a maximum current speed of 1.1 m/s.
Keywords
Introduction
Section snippets
Material and Methods
Materials and methods from the full-text PDF of this article cannot be displayed.
Results
Results from the full-text PDF of this article cannot be displayed.
Discussion
Discussion from the full-text PDF of this article cannot be displayed.
Conclusions
Conclusions from the full-text PDF of this article cannot be displayed.
Acknowledgment
Acknowledgment from the full-text PDF of this article cannot be displayed.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval acknowledgements
No ethical approval required for this article. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5)
Supplementary files
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study, and/or contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References (1)
APHA. 2017. Standard Method for The Examination of Water and Wastewater. 22nd Ed. American Public Health Association Inc. New York.
Damar, A., Colijn, F., Hesse, K. J., & Wardiatno, Y. 2012. The eutrophication states of Jakarta, Lampung and Semangka Bays: Nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics in Indonesian tropical waters. Journal of Tropical Biology & Conservation, 9(1): 61-81.
Duda, A.M., 2016. Policy, Legal and Institutional reform for Public Partnerships Needed to Sustain Large Marine Ecosystems of East Asia. Ocean and Coastal Management, 49: 461-469.
Effendi, H. 2003. Telaah Kualitas Air Bagi Pengelolaan Sumbe rdaya dan Lingkungan Perairan. Kanisius. Yogyakarta.
Humborg, C., Danielsson, A., Sjoberg, B. , & Green, M. 2003. Nutrient lan-sea fluxes in oligothropic and Pristine estuaries of the Gulf of Bothnia, Baltic Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 56: 781-793.
Islam, M.S. 2005. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget in coastal and marine cage aquaculture and impacts of effluent loading on ecosystem: review and analysis towards model development. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50: 48–61.
Isnaeni, N., Suryanti., & Purnomo, P.W. 2015. Kesuburan Perairan Berdasarkan Nitrat, Fosfat, dan KlorofilL-a di Perairan Ekosistem Terumbu Karang Pulau Karimunjawa. Diponegoro Journal of Maquares, 4(2): 75-81.
Lee, D. I., Choi, J. M., Lee, Y. G., Lee, M. O., Lee, W. C., & Kim, J. K. 2008 . Coastal environmental assessment and management by ecological simulation in Yeoja Bay, Korea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 80(4): 495-508.
Mann, K.H. , & Lazier, J.R.N. 1991. Dynamic of Marine Ecosystem. Biological-Physical Interaction in The Oceans. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford.
Millero, F.S. & Sohn, M.L. 1992. Chemical Oceanography. CRC Pr ess. London
Mustofa, A. 2015. Kandungan Nitrat dan Fosfat sebagai Faktor Tingkat Kesuburan Pantai. Jurnal Disprotek, 6(1): 13-19.
Putnam, L.A., Gambrell, R.P., & Rusch, K.A. 2016. CBOD5 treatment using the marshland upwelling sistem. Ecological Engineering, 36: 548-559.
Syakti, A.D., Idris, F., Koenawan, C.J., Asyhar, R., & Apriadi, T. 2019. Biological pollution potential in the water of Bintan-Riau IslandsProvince, Indonesia: First appearance of harmful algal bloom species. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 45 : 117–122
Ulqodry, T. Z., Yulisman, Y., Syahdan, M., & Santoso, S. 2010. Karakterisitik dan sebaran nitrat, fosfat, dan oksigen terlarut di perairan Karimunjawa Jawa Tengah. Jurnal Penelitian Sains, 13(1): 35-41.
Wilkinson, C ., & Salvat, B. 2012. Coastal Resource Degradation in the tropics: Does the tragedy of the commons apply for coral reefs, mangrove forest and seagrass beds. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64: 1096-1105
Bibliographic Information
Cite this article as:
-
Submitted
11 February 2020 -
Published
31 May 2020 -
Version of record
2 September 2020 -
Issue date
31 May 2020
-
Academic subject
Marine Science
Copyright
Sangia Advertisement
Copyright © 2020 Febrianti Lestari. Sangia Research Media and Publishing. Production and hosting by Sangia (SRM™).  This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Comments on this article
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.